| Image | Description |
|---|---|
 |
Salivary extravasation phenomenon (mucous retention phenomenon; mucocele): A well circumscribed blue compressible enlargement of the commissure area. The lesion does not blanch upon pressure. |
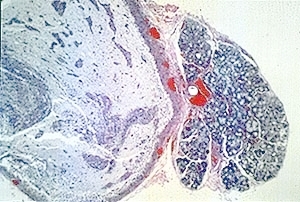 |
Mucous retention (salivary extravasation) phenomenon. Low-power photomicrograph showing a lobule of normal salivary gland tissue adjacent to a circumscribed pool of mucus. Hematoxylin and eosin stain. |
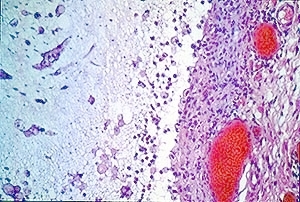 |
Mucous retention (salivary extravasation) phenomenon. Medium-power photomicrograph showing a pool of mucus containing a cellular infiltrate. A wall of fibrovascular connective tissue is adjacent to the mucous pool. Hematoxylin and eosin stain. |
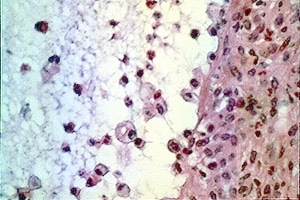 |
Mucous retention (salivary extravasation) phenomenon. High-power photomicrograph showing a pool of mucus containing neutrophils and macrophages with phagocytized mucus. A wall of fibrovascular connective tissue is adjacent to the mucous pool. Hematoxylin and eosin stain. |
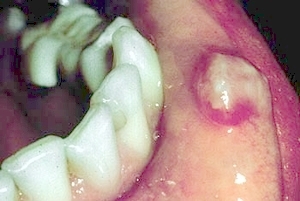 |
Mucous retention (salivary extravasation) phenomenon. A compressible soft tissue enlargement on the lower left lip. |
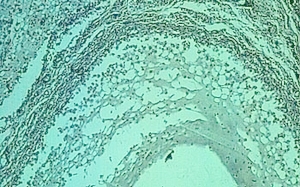 |
Mucous retention (salivary extravasation) phenomenon. Medium-power photomicrograph showing a pool of mucus containing a cellular infiltrate. A wall of fibrovascular connective tissue is adjacent to the mucous pool. Hematoxylin and eosin stain. |
 |
Mucous retention (salivary extravasation) phenomenon. High-power photomicrograph showing a pool of mucus containing neutrophils and macrophages with phagocytized mucus. A wall of fibrovascular connective tissue is adjacent to the mucous pool. Hematoxylin and eosin stain. |
 |
Ranula (salivary extravasation phenomenon; mucous retention phenomenon; mucocele): A large compressible bluish soft tissue enlargement of the floor of the mouth. |